- Why Us?
- Features
White Label
For SaaS Platforms & Agencies
Provide our complete analytics suite to your clients, directly within your own interface and with your/their own branding. Discover Analytics-as-a-Service and White Label Analytics. Great benefit, minimal effort.
- Pricing
- White Label
- Success Stories
- Partner
- ResourcesExpand Your Knowledge
CONTENTS
- What is a Data Breach?
- Data Breach or Data Leak?
- How Common Are Data Breaches?
- Notable Data Breaches in Recent History
- Biggest 10 Data Breaches of all Time
- How Do Breaches Happen?
- Types of Data Breaches
- #1 Phishing Attacks
- #2 Malware Infections
- #3 Ransomware
- #4 Insider Threats
- #5 SQL Injections
- #6 MITM (Man-in-the-Middle Attacks)
- #7 Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
- The Hidden Costs of a Data Breach
- TWIPLA: Your Analytics Partner that Mitigates Data Breach Risks
What Is A Data Breach? Definition, Types, Examples

Did you know that 60% of small companies shut down within six months of a cyber attack?
It's a striking statistic, and there are countless others like it that underline a critical point:
Data breaches pose an existential threat to businesses and can cause significant harm to customers caught in the crossfire.
If you're looking to better understand these threats, this article is a great starting point. You'll discover what data breaches are, how they happen, and just how common they’ve become.
Let’s dive into the breach!
What is a Data Breach?
→ The “Uninvited” Guest
A data breach refers to when data is accessed or stolen without permission.
So it’s theft carried out by hackers - cyber cat burglars who slip past security, get what they came for, and disappear before anyone realizes what’s happening.
They’re like guests at a party they weren’t invited to, gatecrashing to cause trouble, steal valuables, or just for the thrill of it.
But these uninvited guests aren’t always strangers.
Data breach attacks can also be carried out by people you already know. Important data might be:
→ Pulled from stolen devices
→ Accessed by employees, or
→ Exposed through scams that trick users into handing over sensitive information.
We’ll explore the different types of breaches in more detail later, but it’s crucial to remember one thing: the internet is a dangerous place for your data.
When one occurs, the consequences of a data breach for businesses - large or small - can be severe: reputational damage, financial losses, operational disruptions, and legal repercussions.
Data Breach or Data Leak?
Secure data storage is an essential business requirement.
But servers can always be deliberately breached, and data can also simply leak out through lack of care.
Admittedly, the consequences can often be the same for businesses.
And while the terms “data breach” and “data leak” are often used interchangeably, they actually refer to different types of security incidents.
Let's look at the data breach and data leak meanings:
→ A breach occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive information.
This involves the deliberate theft or exposure of data, which can lead to serious consequences such as identity theft, financial loss, or reputational damage.
Often, this personal data is traded on the dark web.
→ A data leak results from the unintentional exposure of data.
But how does a data leak happen?
They're normally possible because of poor security practices, system misconfigurations, or human error.
And while a dataleak doesn’t always involve an external attack, it still poses significant risks as sensitive information becomes accessible without proper authorization.
As you can see, the difference comes down to intent.
But deliberate or not, the event will be just as damaging if the data is then misused.
What’s important is understanding the source and nature of the incident, which enables businesses to both manage its impact and prevent something similar from happening in the future.
How Common Are Data Breaches?
Data breaches are common, and more and more businesses are affected every year.
Take the US for instance. A report from the Identity Theft Resource Center found that there were more reported data breaches in 2023 than ever before, with 3,205 businesses successfully targeted.
These incidents affected 353 million victims, making data breaches the most widespread crime - impacting more people than any other type of offense.
Or take the UK, where an estimated 22% of businesses have experienced cyber crime in the last 12 months (GOV.UK).
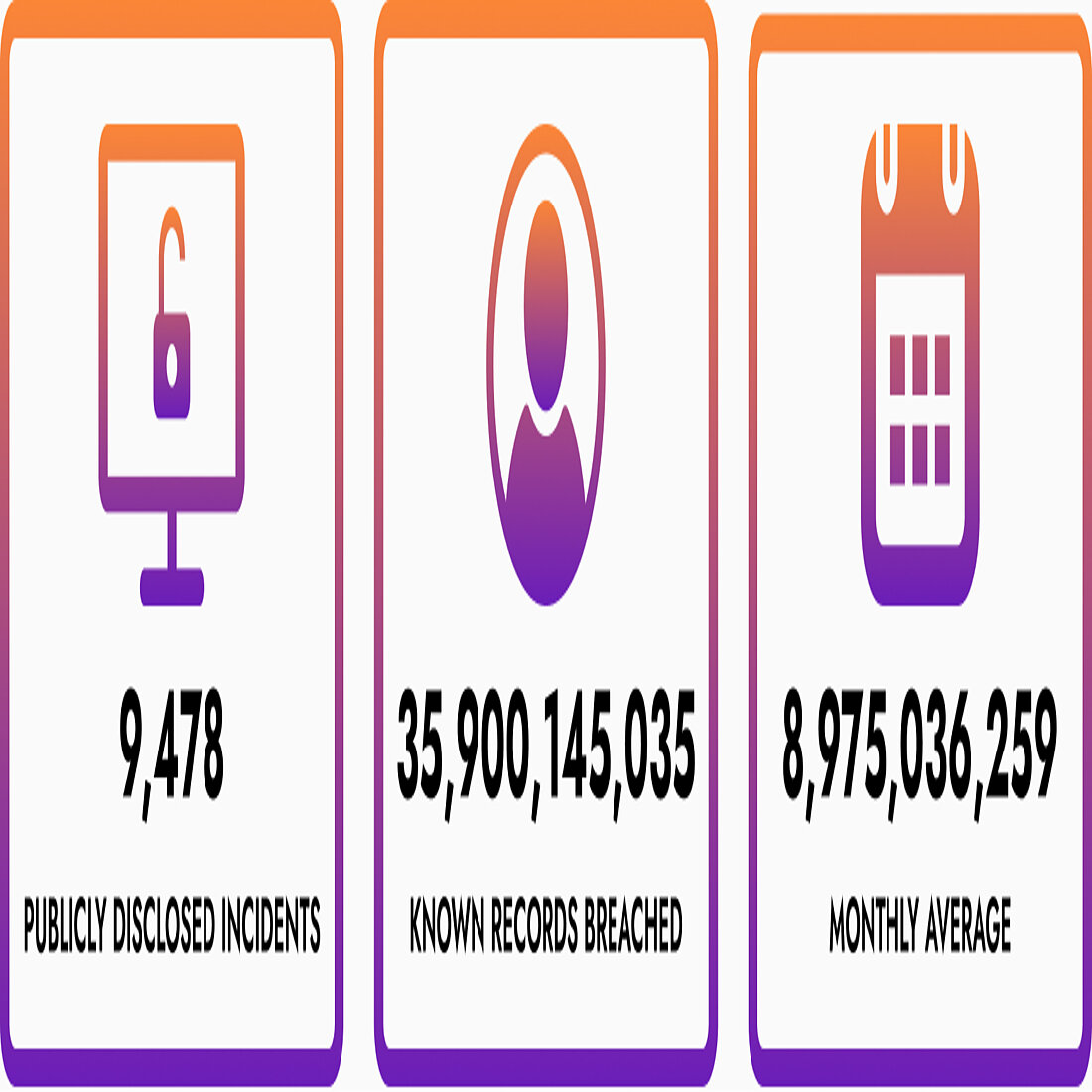
Global Data Breaches in 2024
But cybercrime doesn't only happen in the English-speaking world, with Russians, Ukrainians, the Chinese, and Nigerians suffering more of these incidents than anyone else.
And while we're only in Q3, data from IT Governance suggests that 2024 will be another record year for global breaches:
Every year, data breaches impact businesses and individuals across the world.
Many companies are unable to recover and close down. People’s lives can also be ruined and these data breaches serve as cautionary tales, highlighting the importance of protecting data through strong cybersecurity measures.
And while most data breaches fly under the radar of public consciousness, some are so huge that they make front page headlines. For reference, here's just two of the many stories that we've covered here at TWIPLA:
- Norway Fining Meta $98,500 per day for User Privacy Breach
- WhatsApp Data Breach Affects 487 Million Users
But that's obviously only the tip of the iceberg.
Below are some of the most significant data breaches in recent history, each leaving a lasting impact on the organizations involved and their customers.
Biggest 10 Data Breaches of all Time
# | Company | Year | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Yahoo | 2013 | 3 billion accounts |
2 | Aadhaar | 2018 | 1.1 billion Indian citizens |
- | Alibaba | 2019 | 1.1 billion pieces of user data |
4 | 2021 | 700 million users | |
5 | Sina Weibo | 2020 | 538 million accounts |
6 | 2019 | 533 million users | |
7 | Marriott International | 2018 | 500 million customers |
- | Yahoo | 2014 | 500 million accounts |
9 | Adult Friend Finder | 2016 | 412.2 million accounts |
10 | MySpace | 2013 | 360 million user accounts |
The first thing that stands out from this list is the sheer number of people affected by these data breaches.
If we pretend for a moment that there’s no overlap, then most people in the world had their data compromised - and that’s from only 10 breaches, big though they were.
The second thing that stands out is how recent most of these data breaches were.
While the internet has been popular since the late 1990s, all 10 of the biggest data breaches in history have happened in the last ten years.
This isn’t a coincidence.
“There were 5 exabytes of information created between the dawn of civilization through 2003, but that much information is now created every two days.”
- Eric Schmidt, Executive Chairman at Google
We’re in the era of big data, with over 2,560 terabytes of data created daily.
For context, some technologists have estimated that all the words ever spoken by mankind would equal half that figure.
Much of this data is stored online, making breaches more frequent and damaging than ever before.
How Do Breaches Happen?
Data protection is an ongoing arms race between service providers and the cyber criminals trying to beat their systems.
It’s also a test for businesses looking to protect their most valuable asset from unauthorized access by employees, contractors, and other parties.
But in practice, data breaches result from a variety of security failures or vulnerabilities that businesses haven’t accounted for.
These breaches often occur when gaps in an organization’s cybersecurity defenses are exploited, whether due to:
→ Human error
→ Weak policies, or
→ Sophisticated cyberattacks.
Common triggers for data breaches include poor system configurations, unpatched software, or accidental exposure of sensitive data.
In many cases, breaches stem from exploiting weak points in an organization’s security infrastructure, such as:
→ Insufficient encryption
→ Weak authentication methods, or
→ Inadequate monitoring.
Human factors also play a significant role.
Attackers frequently use tactics like phishing or social engineering to deceive individuals into revealing confidential information.
Additionally, insufficient oversight of third-party vendors or partners can lead to unintended exposure of data if those external systems are compromised.
By understanding how breaches occur, organizations can take steps to reinforce their defenses and minimize potential risks.
Types of Data Breaches
→ A Digital Disaster Menu
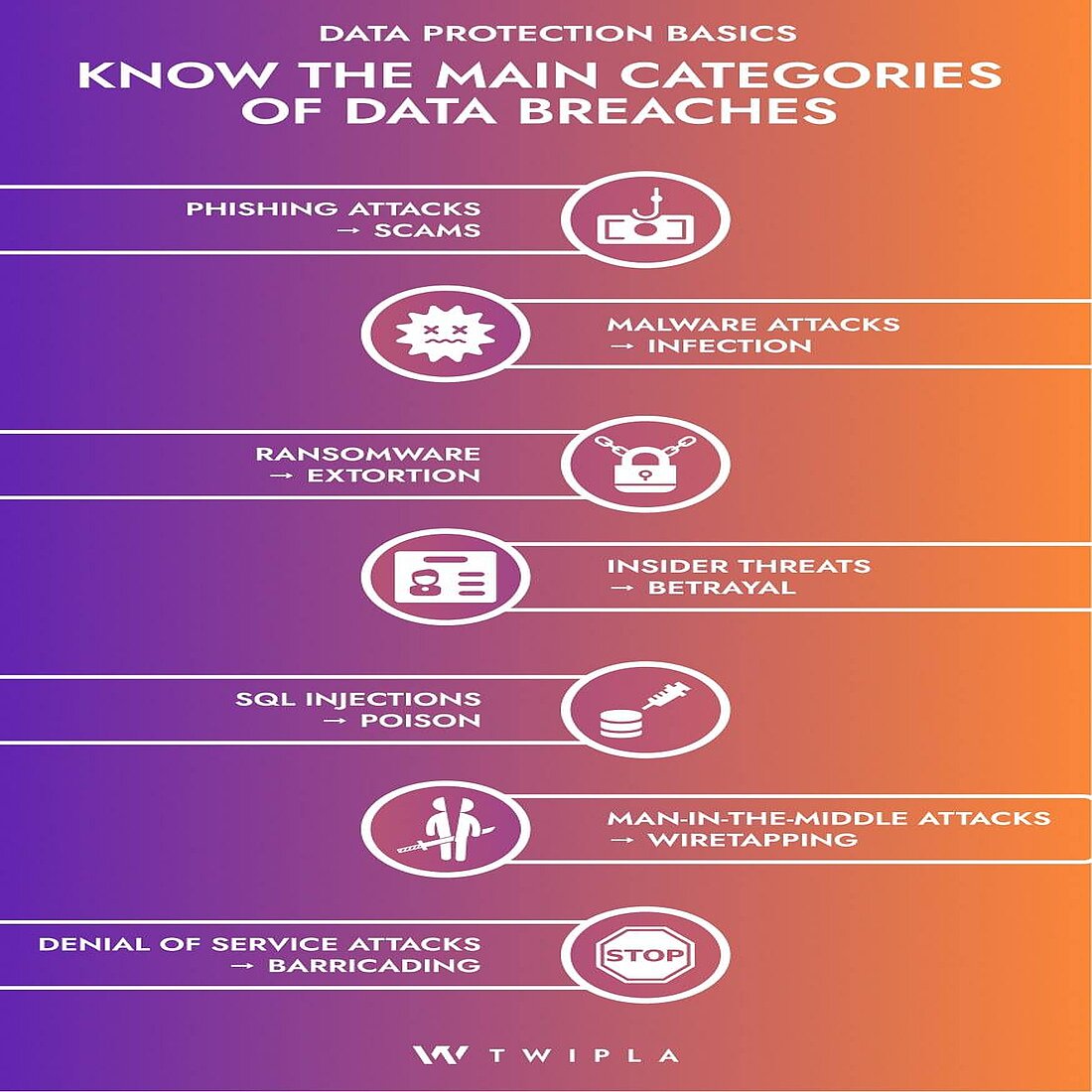
Unfortunately, data breaches can arrive in a wide variety of forms.
Each category attacks different vulnerabilities, and businesses can only make their data watertight by implementing policies and processes that protect them from each category at every stage of the data lifecycle.
Below, you’ll find information about the seven main categories of data breaches.
#1 Phishing Attacks
3.4 billion phishing emails are sent every day.
- AAG-IT
Phishing attacks are scams.
They trick people into providing sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers by pretending to be a legitimate source.
Attackers often send emails or messages that appear to come from trusted companies, urging recipients to click a link or provide personal data.
Once the user is deceived, the attackers gain access to their account or confidential information. These attacks rely heavily on social engineering and can be difficult to spot without proper awareness.
Example Phishing Attack: Colonial Pipeline
The most successful phishing attack in history was suffered by the largest pipeline system for refined oil products in the US.
In May 2021, their operation ground to a halt as the result of ransomware, made possible by a successful phishing attack that gave hackers password access.
It's estimated that this breach cost the company $3.4 billion.
#2 Malware Infections
In 2023, 6.06 billion malware attacks were detected worldwide
- Statista
Malware is short for "malicious software," and it refers to any harmful program designed to infiltrate or damage a computer system.
Common types of malware include viruses, worms, and spyware.
Once installed on a device, malware can steal sensitive data, monitor activities, or cause disruption.
Malware infections often occur when users unknowingly download malicious software through email attachments, compromised websites, or unverified downloads.
Example Malware Attack: WannaCry
Unlike earlier ransomware attacks that affected devices individually, the 2017 WannaCry attack was able to propagate through networks and this cryptoworm infected over 200,000 computers globally.
The attack took advantage of a Windows vulnerability that Microsoft had already addressed with a patch.
Many users, however, had not updated their systems, leaving their computers exposed.
WannaCry is considered one of the most damaging and infamous ransomware attacks ever, with estimated costs around $4 billion.
#3 Ransomware
Global ransomware attacks rose by 74% between 2022 and 2023.
Ransomware is a type of malware that locks or encrypts a user’s data, making it inaccessible until a ransom is paid to the attacker.
The attacker usually demands payment in cryptocurrency and threatens to permanently delete or leak the data if the ransom isn't paid.
Ransomware attacks can target both individuals and organizations, leading to severe disruptions and data loss. It's important never to pay the ransom, as it doesn’t guarantee the safe return of the data.
Example Ransomware Attack: ExPetr
In June 2017, the ExPetr ransomware, also known as NotPetya, disrupted global operations. Unlike traditional ransomware, ExPetr was designed to cause maximum damage rather than demand ransom. Originally aimed at Ukraine, its impact quickly spread beyond control.
NotPetya, a wiper disguised as ransomware, targeted Windows systems by exploiting the EternalBlue SMB vulnerability. It rapidly encrypted the master boot record (MBR), rendering affected systems unbootable and used tools like Mimikatz to steal credentials and spread through networks.
Major casualties included global shipping firm Maersk and pharmaceutical company Merck, with Maersk reporting about $300 million in losses. Overall, NotPetya's financial impact is estimated at around $10 billion, making it the costliest cyberattack in history.
#4 Insider Threats
Internal actors account for 19% of all data breaches.
Insider threats come from individuals within an organization who have access to sensitive data.
This could be an employee, contractor, or business partner.
Insider threats can be intentional, such as when someone steals data for personal gain, or unintentional, like when someone accidentally leaks confidential information through careless actions.
Because insiders already have access, these threats can be harder to detect than external attacks.
Example Insider Threat: Boeing
In 2017, a Boeing employee sent a spreadsheet to his wife for help with a formatting issue he was having, without realizing that it contained personal information of about 36,000 coworkers.
The spreadsheet had hidden columns with sensitive data, including employee IDs, birthplaces, and social security numbers.
Although Boeing believes the data remained confined to the two devices involved, the company provided two years of free credit monitoring to all employees included in the leaked database, totaling an estimated $7 million in costs.
#5 SQL Injections
SQL injection was the biggest threat to web applications in 2023, making up 23% of all attacks.
- Statista
SQL injection is a technique used by attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in a website’s database.
By inserting malicious code into an input field, attackers can manipulate the database to reveal sensitive information or corrupt data.
Websites that don’t properly validate or sanitize user inputs are vulnerable to this type of attack, which can result in the exposure of sensitive data like customer records or login credentials.
Example SQL Injection Attack: Heartland
In 2008, Heartland Payment Systems experienced one of the largest data breaches in history due to an SQL injection attack.
This breach exposed around 130 million credit and debit card numbers, highlighting the severe vulnerabilities in digital payment systems.
The incident, reported by Proofpoint, emphasized that no organization is immune to cyber threats and underscored the need for stronger cybersecurity measures in the financial sector.
#6 MITM (Man-in-the-Middle Attacks)
35% of exploitation activity involves Man-in-the-Middle attacks.
In a Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack, an attacker secretly intercepts the communication between two parties, such as between a user and a website, without either party knowing.
The attacker can eavesdrop on or even alter the communication, potentially stealing sensitive data like passwords or financial information.
MITM attacks often occur over unsecured Wi-Fi networks, where the attacker can easily monitor traffic.
Example Man-in-the-Middle Attack: NSA
In 2013, Edward Snowden leaked documents from his time as a consultant at the National Security Agency (NSA).
These documents revealed that the NSA had impersonated Google to intercept traffic by spoofing SSL encryption certificates.
This man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack allowed the NSA to access search records of all Google users, including U.S. citizens, constituting illegal domestic surveillance.
#7 Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Microsoft alone responds to an average of 1,700 Denial of Service attacks every day.
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack floods a website or online service with an overwhelming amount of traffic, causing it to crash or become unavailable.
The goal is to disrupt the normal operation of the service, often resulting in significant downtime for the targeted website.
DoS attacks don’t typically steal data, but they can lead to financial losses and damage a company’s reputation by making their services inaccessible to legitimate users.
Example Denial of Service Attack: Dyn
In October 2016, a DoS attack targeted Dyn, a DNS provider responsible for managing the domain names of various companies.
The attack overwhelmed Dyn’s servers with excessive traffic, causing a major web outage and disrupting over 80 websites.
Major sites affected included Twitter (now X), Amazon, Spotify, Airbnb, PayPal, and Netflix.
The Hidden Costs of a Data Breach
→ More Than Just a Bad Day
Given that newspaper headlines - for obvious reasons - focus on mega data breaches of well known companies, it’s easy to believe that these incidents only affect large corporations.
Unfortunately, the reality is very different.
In fact, 46% of all cyber breaches impact businesses with fewer than 1,000 employees.
It’s easy to see why: smaller companies normally have weaker security systems, making them easy prey for skilled hackers.
But this statistic also highlights the unappetizing truth that no company is immune to the risks associated with data breaches.
And while the immediate disruption is bad enough, the consequences of a data breach go much deeper.
For businesses that lack robust security measures, the fallout can be severe and multifaceted:
Financial Loss
The average cost of a data breach is $4.88 million
The direct costs of a data breach can be staggering.
Expenses may include fines, legal fees, and compensation to affected customers. And when combined, data breaches can cost millions of dollars, making these events particularly devastating for smaller companies.
Reputational Damage
80% of customers will stop associating with a business if their information is compromised in a data breach
- International Data Corporation (IDC)
Trust is a critical component of any business relationship. A data breach can severely damage your company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and potential long-term damage to your brand. Rebuilding a damaged reputation can be a slow and costly process, often requiring significant investments in public relations and marketing.
Operational Disruption
70% of businesses have their ability to function either moderately or severely affected by a data breach.
- IBM Cost of Data Breach Report 2024
A data breach can cause significant operational disruptions. This may involve downtime as systems are secured and repaired, loss of productivity, and the need for immediate IT support. Small businesses, in particular, may struggle to manage these disruptions effectively, impacting their overall performance.
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
20% of organizations that experienced a data breach paid $250k or more in regulatory fines.
- IBM Security - Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023
Data privacy is a vital consideration for businesses, and this includes compliance with data protection legislation. A breach can lead to legal action from regulatory bodies and affected individuals. Non-compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA can result in substantial fines and legal penalties, further straining a business’s resources.
Loss of Competitive Advantage
87% of internet users said they would not do business with a company if they had concerns about its security practices.
- McKinsey, The consumer-data opportunity and the privacy imperative
Exposed data can provide competitors with sensitive insights into your operations, potentially eroding your competitive edge. Additionally, if proprietary information is compromised, it can undermine your market position and innovation efforts.
Increased Security Costs
Following an incident, businesses often need to invest heavily in upgrading their security measures as a means of data breach prevention.
This can include implementing new technologies, conducting security audits, and training staff, which adds to the financial burden.
As you can see, the impact of a data breach is profound and far-reaching.
It’s crucial for businesses of all sizes to invest in strong security measures to protect against potential breaches and mitigate the associated risks.
No company is too small to be targeted, and effective security practices are essential for safeguarding both your data and your business’s future.
TWIPLA: Your Analytics Partner that Mitigates Data Breach Risks
Choosing the right website analytics platform is crucial for protecting customer data and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. TWIPLA stands out as an ideal choice for businesses aiming to minimize data breach vulnerability and the impact of these incidents.
- Privacy-Flexible Design: TWIPLA is built from the ground up with adaptable data protection controls, giving you flexibility over privacy and security requirements.
- Encryption: Our platform uses advanced anonymization techniques to scrub personal identifiers from data.
- Data Minimization: Our platform adheres to the principle of data minimization, collecting only the data necessary for digital insights.
- ISO Certification: Our commitment to the highest standards of data protection and security is underscored by our ISO certification.
- Comprehensive Solution: TWIPLA offers a complete analytics platform that integrates seamlessly, eliminating the need for additional tools and streamlining operations.
By choosing TWIPLA, you benefit from enhanced data security and a trusted partner dedicated to safeguarding your information. Our approach not only strengthens your defenses but also provides peace of mind, knowing your data is in safe hands.
Share article
Get Started for Free
Gain World-Class Insights & Offer Innovative Privacy & Security











